SITCOMTN-144
WET-007 Compare CWFS approaches with WET-001 LsstCam data#
Last verified to run 2024/11/19
Versions:
lsst_distrib w_2024_46 (ext, cvmfs)
ts_wep v13.0.1 (commit c0670ffe)
This document compares using TIE and Danish to analyze simulated WET-001 data. Given the availability of the OPD (“truth”), goodness of fit is measured by the fidelity to the OPD. The simulation included 800 data references, i.e. 8 detectors (corner sensors) for 100 random optical states. This technote is part of documentation describing a comparison between TIE and Danish (and ML in some cases) using simulated and observed data. The advantage of simulated data is a cleaner sample and exact knowledge of the input optical state in the form of OPD, thus enabling testing the fidelity of CWFS fit.
Imports#
from lsst.daf import butler as dafButler
from lsst.ts.wep.task.generateDonutDirectDetectTask import (GenerateDonutDirectDetectTask,GenerateDonutDirectDetectTaskConfig)
from lsst.ts.wep.utils import convertZernikesToPsfWidth
from copy import copy
from lsst.obs.lsst import LsstCam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from astropy.visualization import ZScaleInterval
from matplotlib import colormaps as cmaps
import numpy as np
from astropy.io import fits
Ingest raws, run ISR#
Employ the central AOS butler repository. The simulated data was ingested with
butler ingest-raws /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/ /sdf/data/rubin/user/gmegias/projects/commissioning_sims/WET-001_lsstcam/state_100/amp*
butler define-visits /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim lsst.obs.lsst.LsstCam
butler ingest-raws /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/ /sdf/data/rubin/user/gmegias/projects/commissioning_sims/WET-001_lsstcam/state_100/amp*
To run ISR, we use bps condor .
Make site_bps.yaml, containing
site:
s3df:
profile:
condor:
+Walltime: 7200
Run
allocateNodes.py -v -n 10 -c 64 -m 60:00:00 -q milano -g 1800 s3df --account rubin:developers
bps submit site_bps.yaml -b /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim -i LSSTCam/raw/all,LSSTCam/calib/unbounded -o WET-001_lsstCam_ISR -p /sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007/lsstPipelineISRdoVar.yaml -d "instrument='LSSTCam' and exposure.science_program = 'wet001_100_dof_states'"
Run donut detection in interactive mode to test sigma levels#
We first run donut detection interactively for a single state to test the correct setting to use, for instance config.measurementTask.nPixMinDetection, or config.measurementTask.nSigmaDetection.
dataRefs = butler.registry.queryDatasets('postISRCCD', collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_ISR'],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' and exposure.science_program = 'wet001_100_dof_states' \
and exposure.seq_num = 2001 and detector = 192").expanded()
ref = list(dataRefs)[0]
exp = butler.get('postISRCCD', dataId = ref.dataId, collections = ['WET-001_lsstCam_ISR'])
zscale = ZScaleInterval()
camera = LsstCam().getCamera()
config = GenerateDonutDirectDetectTaskConfig()
config.measurementTask.nSigmaDetection = 5
config.donutSelector.useCustomMagLimit = True
fig = plt.figure()
d = exp.image.array
vmin,vmax = zscale.get_limits(d)
plt.imshow(d, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, origin='lower')
# detect all donuts and overplot
config.doDonutSelection = False
task = GenerateDonutDirectDetectTask(config=config)
taskOut = task.run(copy(exp), camera)
plt.scatter(taskOut.donutCatalog['centroid_x'], taskOut.donutCatalog['centroid_y'],
marker='+', c='r', label=f'doDonutSelection:{config.doDonutSelection}'
)
# show the impact of turning on donut selector
config.doDonutSelection = True
task = GenerateDonutDirectDetectTask(config=config)
taskOut = task.run(copy(exp), camera)
plt.scatter(taskOut.donutCatalog['centroid_x'], taskOut.donutCatalog['centroid_y'],
marker='o', s=100, facecolors='none', edgecolors='magenta' ,label=f'doDonutSelection:{config.doDonutSelection}'
)
plt.xlabel('x [px]')
plt.ylabel('y [px]')
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=[1.0,0.5])
plt.title(f'det {detId}')
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.measurementTask:Found 20 sources in exposure
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.measurementTask:Measured 20 of 20 sources in exposure
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.measurementTask:Found 20 sources in exposure
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.measurementTask:Measured 20 of 20 sources in exposure
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask:Running Donut Selector
INFO:lsst.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.donutSelector:Selected 12/20 references
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'det 191')
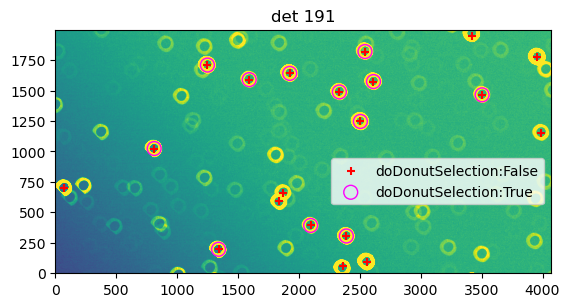
Thus we see that \(5\sigma\) threshold selects many donuts, while the effect of donut selector is the disappearance of donuts too close to the edge.
Run donut detection, cutouts, and Zernike estimation#
We run each step separately, to be able to reuse the postISRCCD, donutStampsExtra, and donutStampsIntra.
To run bps we need to run:
cd /sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007
allocateNodes.py -v -n 10 -c 64 -m 60:00:00 -q milano -g 1800 s3df --account rubin:developers
lsst
aos
isrCollection = "WET-001_lsstCam_ISR"
cutoutsCollection = "WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps"
tieCollection = "WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1"
danishCollection = "WET-001_lsstCam_direct_Danish1"
isrYaml = "lsstPipelineISRdoVar.yaml"
cutoutYaml = "lsstPipelineDirectCutoutOnly.yaml"
danishYaml = "lsstPipelineCalcDanishOnly.yaml"
tieYaml = "lsstPipelineCalcTieOnly.yaml"
pathCwd = '/sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007'
isrYamlPath = os.path.join(pathCwd, isrYaml)
cutoutYamlPath = os.path.join(pathCwd, cutoutYaml)
danishYamlPath = os.path.join(pathCwd, danishYaml)
tieYamlPath = os.path.join(pathCwd, tieYaml)
cmdCutout = f"bps submit site_bps.yaml -b {butlerRootPath} -i {isrCollection},LSSTCam/calib/unbounded \
-o {cutoutsCollection} -p {cutoutYamlPath}"
cmdDanish = f"bps submit site_bps.yaml -b {butlerRootPath} -i {cutoutsCollection} \
-o {danishCollection} -p {danishYamlPath} "
cmdTie = f"bps submit site_bps.yaml -b {butlerRootPath} -i {cutoutsCollection} \
-o {tieCollection} -p {tieYamlPath}"
print(cmdCutout, "\n")
print(cmdDanish, "\n")
print(cmdTie, "\n")
bps submit site_bps.yaml -b /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/ -i WET-001_lsstCam_ISR,LSSTCam/calib/unbounded -o WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps -p /sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007/lsstPipelineDirectCutoutOnly.yaml
bps submit site_bps.yaml -b /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/ -i WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps -o WET-001_lsstCam_direct_Danish1 -p /sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007/lsstPipelineCalcDanishOnly.yaml
bps submit site_bps.yaml -b /sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/ -i WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps -o WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1 -p /sdf/group/rubin/shared/scichris/DM-46763_WET-007/lsstPipelineCalcTieOnly.yaml
The lsstPipelineDirectCutoutOnly.yaml contains:
description: detect and cutout donuts
instrument: lsst.obs.lsst.LsstCam
tasks:
generateDonutDirectDetectTask:
class: lsst.ts.wep.task.generateDonutDirectDetectTask.GenerateDonutDirectDetectTask
config:
donutSelector.useCustomMagLimit: True
measurementTask.nSigmaDetection: 5
cutOutDonutsCwfsTask:
class: lsst.ts.wep.task.cutOutDonutsCwfsTask.CutOutDonutsCwfsTask
The lsstPipelineCalcDanishOnly.yaml contains:
description: estimate Zk with Danish only
instrument: lsst.obs.lsst.LsstCam
tasks:
calcZernikesTask:
class: lsst.ts.wep.task.calcZernikesTask.CalcZernikesTask
config:
python: |
from lsst.ts.wep.task import EstimateZernikesDanishTask
config.estimateZernikes.retarget(EstimateZernikesDanishTask)
aggregateZernikesTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateZernikesTask
aggregateDonutCatalogsTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateDonutCatalogsTask
aggregateAOSVisitTableTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateAOSVisitTableTask
plotAOSTask: lsst.donut.viz.PlotAOSTask
aggregateDonutStampsTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateDonutStampsTask
plotDonutTask: lsst.donut.viz.PlotDonutTask
The lsstPipelineCalcTieOnly.yaml contains:
description: estimate Zk with TIE only
instrument: lsst.obs.lsst.LsstCam
tasks:
calcZernikesTask:
class: lsst.ts.wep.task.calcZernikesTask.CalcZernikesTask
config:
python: |
from lsst.ts.wep.task import EstimateZernikesTieTask
config.estimateZernikes.retarget(EstimateZernikesTieTask)
aggregateZernikesTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateZernikesTask
aggregateDonutCatalogsTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateDonutCatalogsTask
aggregateAOSVisitTableTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateAOSVisitTableTask
plotAOSTask: lsst.donut.viz.PlotAOSTask
aggregateDonutStampsTask: lsst.donut.viz.AggregateDonutStampsTask
plotDonutTask: lsst.donut.viz.PlotDonutTask
Inspect the outputs#
butlerRootPath = '/sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/'
butler = dafButler.Butler(butlerRootPath)
dataRefs = butler.registry.queryDatasets('donutStampsExtra', collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps'],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' and visit.seq_num = 2002").expanded()
ref = list(dataRefs)[0]
donutStampsExtra = butler.get('donutStampsExtra', dataId=ref.dataId, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_stamps'])
fig,axs = plt.subplots(5,5, figsize=(15,15))
ax = np.ravel(axs)
i=0
donutStamps = donutStampsExtra
for stamp in donutStamps:
ax[i].imshow(stamp.stamp_im.image.array, origin='lower')
i += 1
if len(donutStamps)<len(ax):
for i in range(len(donutStamps), len(ax)):
ax[i].axis('off')
Check if all states have Zernike estimates#
butlerRootPath = '/sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/'
butler = dafButler.Butler(butlerRootPath)
for method in ['Danish', 'TIE']:
dataRefs = butler.registry.queryDatasets('zernikeEstimateRaw', collections=[f'WET-001_lsstCam_direct_{method}1'],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' ").expanded()
refs=[]
for ref in dataRefs:
refs.append(ref)
n = len(refs)
print(f'There are {n} Zk estimates for {method}')
There are 396 Zk estimates for Danish
There are 396 Zk estimates for TIE
Since there were 792 raw images, half (one Zk estimate per sensor pair) would be 396.
Compare TIE to Danish#
Read the OPD values :
# load all OPDs to a dict
all_opd = {}
for n in range(1,101):
opdDir = f'/sdf/data/rubin/user/gmegias/projects/commissioning_sims/WET-001_lsstcam/state_{n}'
hdul = fits.open(os.path.join(opdDir,'opd.fits'))
opds = {}
for i in range(len(hdul)):
opd_zks_1_28 = []
for key,value in hdul[i].header.items():
if key.startswith('AZ'):
#print(key.split('_')[1])
opd_zks_1_28.append(value)
opds[i] = opd_zks_1_28
all_opd[n] = opds
opd_raft_to_id = {'R00':0, 'R04':1, 'R40':2, 'R44':3}
Read the results:
butlerRootPath = '/sdf/data/rubin/repo/aos_imsim/'
butler = dafButler.Butler(butlerRootPath)
registry = butler.registry
output_collection = 'WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'
dataRefs = list(registry.queryDatasets('donutStampsExtra', collections=[output_collection],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' and detector.purpose='WAVEFRONT' ").expanded())
print(len(dataRefs))
396
results = {'tie':{}, 'danish':{}}
for method in results.keys():
results[method] = {}
for state in range(1,100):
results[method][state] = {}
for ref in dataRefs:
# read in the results of each method
for method in results.keys():
if method == 'tie':
coll_method = 'TIE'
else:
coll_method = 'Danish'
coll = f'WET-001_lsstCam_direct_{coll_method}1'
state = int(str(ref.dataId.visit.id)[-3:])
raft = ref.dataId.detector.raft
results[method][state][raft] = butler.get('zernikeEstimateAvg',
dataId=ref.dataId,
collections=[coll])
Compare TIE to Danish:
def plot_lsstcam_fit_vs_opd(state, opd_raft_to_id, all_opd, results, plot_asec=False):
rafts = ['R04', 'R44', 'R00','R40']
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(16,8))
ax = np.ravel(axs)
i=0
# this plots just the pairing results
colors = {'danish':'green', 'tie':'orange'}
for raft in rafts:
ax[i].set_title(raft )
opdId = opd_raft_to_id[raft]
opd_zk = 0.001*np.array(all_opd[state][opdId][3:29])
dFWHMtrue = convertZernikesToPsfWidth(opd_zk)
for method in results.keys():
avg_zk = results[method][state][raft][0]
# Convert Zernikes to image quality contribution (asec) with `convertZernikesToPsfWidth`
if plot_asec:
dFWHMfit = convertZernikesToPsfWidth(avg_zk)
diffFWHM = dFWHMfit - dFWHMtrue
psfDegradation = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(diffFWHM)))
ax[i].plot(np.arange(4,29), diffFWHM, marker='d', label=f'{method} PSF FWHM degradation {psfDegradation:.3f} asec')
else:
diff_zk = avg_zk-opd_zk
rms_diff_avg = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.square(avg_zk-opd_zk)))
ax[i].plot(np.arange(4,29), diff_zk, marker='d', label=f'{method} $\Delta$rms={rms_diff_avg:.3f} microns')
if plot_asec:
ax[i].set_ylabel(r'$\Delta$ (PSF fit - PSF OPD) [asec]')
else:
ax[i].set_ylabel(r'$\Delta$ (fit-OPD) [microns]')
ax[i].set_xlabel('Zk mode')
ax[i].set_xticks(np.arange(4,29,step=2))
ax[i].axhline(0,ls='--', c='red')
ax[i].legend()
i+=1
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3)
fig.suptitle(f'WE7-007 lsstCam, state {state}:, \n TIE vs Danish')
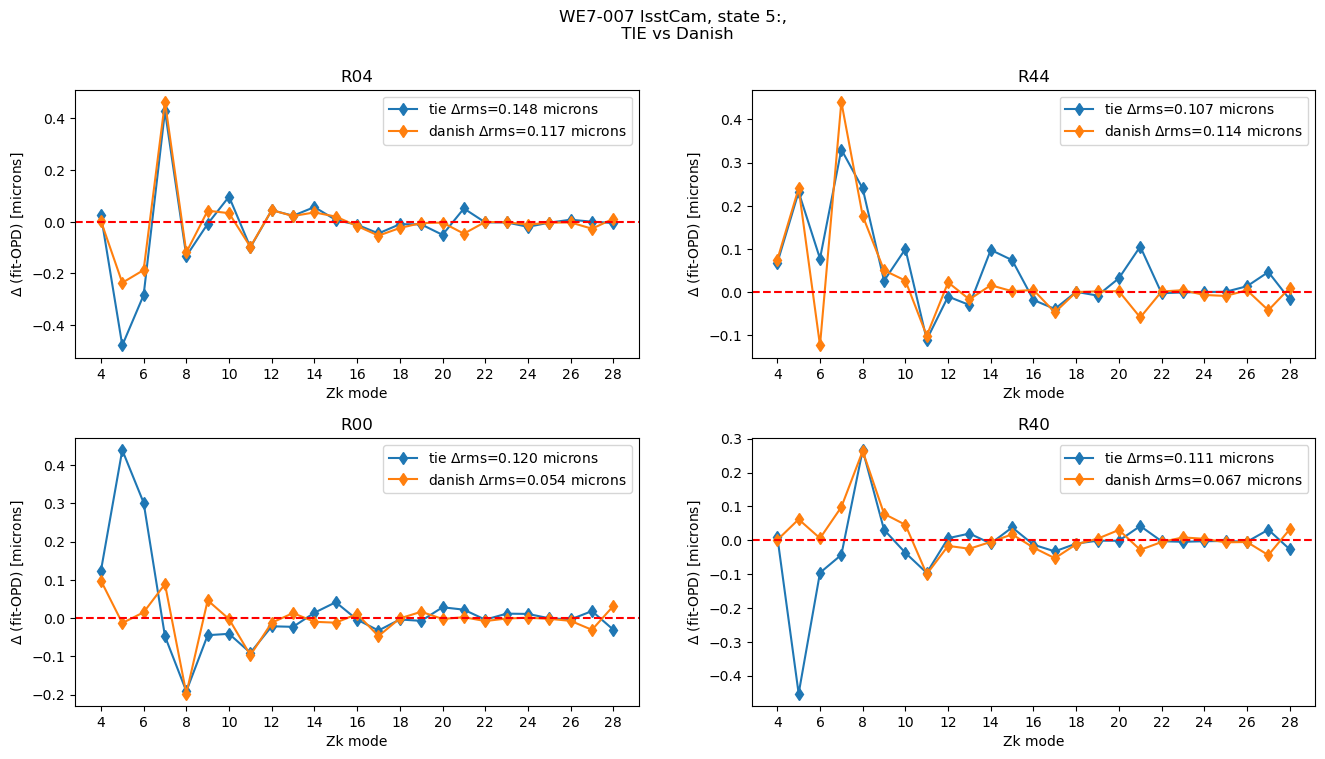
Plot comparison between TIE and Danish, showing the difference from the OPD for a single state:
plot_lsstcam_fit_vs_opd(5, opd_raft_to_id, all_opd, results)
plot_lsstcam_fit_vs_opd(5, opd_raft_to_id, all_opd, results, plot_asec=True)
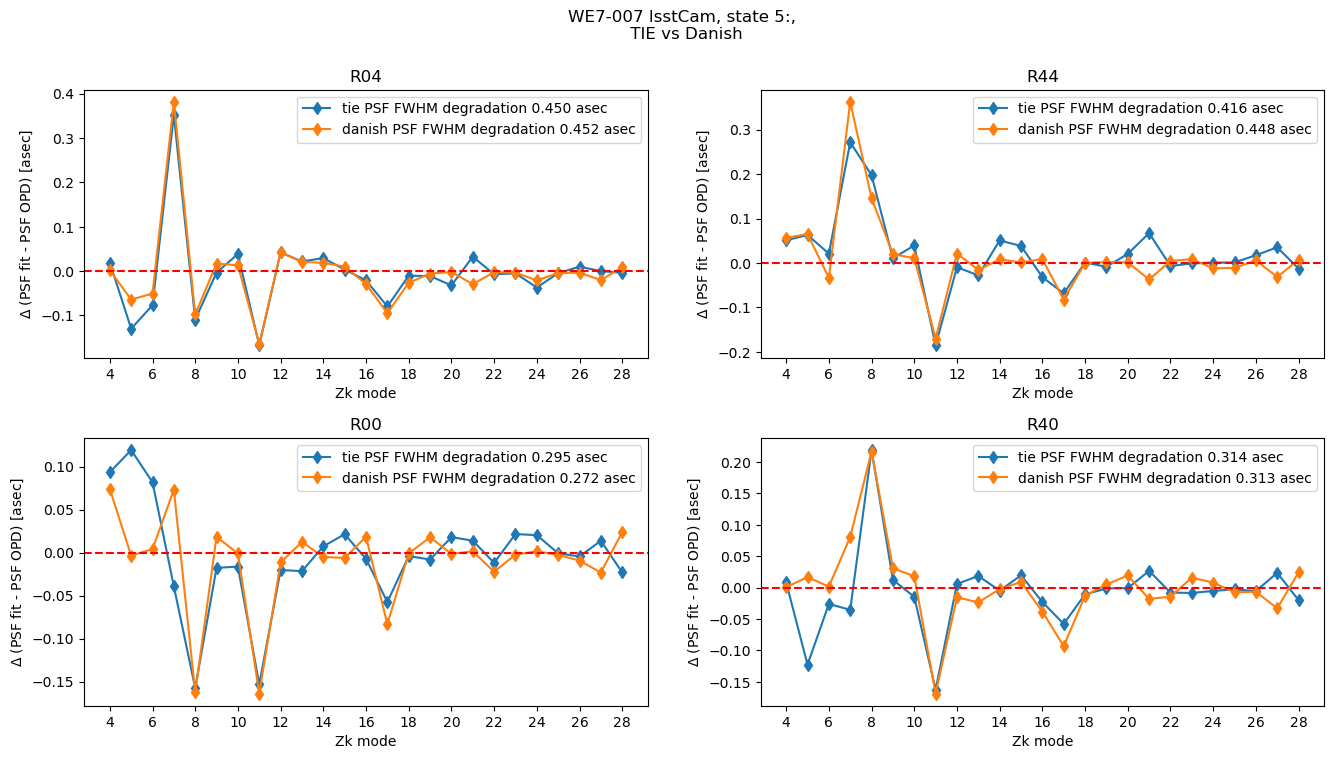
For each state we have one RMS difference between fitted value and the OPD:
The PSF FWHM degradation is the AOS contribution, i.e. degradation with respect to the optimal PSF:
where we sum over all available Zernike modes. We can calculate both quantities for all states:
rmss={}
psfDeg={}
rafts = ['R04', 'R44', 'R00','R40']
# add pairing results
for algo in results.keys():
rmss[algo] = {}
psfDeg[algo]={}
for raft in rafts:
rmss[algo][raft] = []
psfDeg[algo][raft] = []
opdId = opd_raft_to_id[raft]
for state in results[algo].keys():
opd_zk = 0.001*np.array(all_opd[state][opdId][3:29])
avg_zk = np.mean(results[algo][state][raft], axis=0)
rms_diff = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.square(avg_zk-opd_zk)))
rmss[algo][raft].append(rms_diff)
dFWHMtrue = convertZernikesToPsfWidth(opd_zk)
dFWHMfit = convertZernikesToPsfWidth(avg_zk)
diffFWHM = dFWHMfit - dFWHMtrue
psfDegradation = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(diffFWHM)))
psfDeg[algo][raft].append(psfDegradation)
if rms_diff > 10:
print(algo, raft, state, rms_diff)
tie R04 45 1289.5422211020345
tie R44 45 113.45955258359294
tie R00 45 251.4142584734439
tie R40 45 101.10504202327914
Plot a summary RMS difference per state for all states: this highlights if there is any particular optical state that either algorithm performed more poorly:
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(16,10))
ax = np.ravel(axs)
for method in rmss.keys():
i=0
for raft in rafts:
ax[i].plot(results[algo].keys(), rmss[method][raft], marker='s', label=f'{method}')
ax[i].set_title(raft)
ax[i].set_ylim(-0.1,1.5)
i+=1
fig.text(0.5,0.06,'state #', fontsize=17)
fig.text(0.06,0.5,r'RMS ($\Delta$(zk-opd) ) [microns] ', rotation=90, fontsize=17, va='center')
fig.suptitle('CWFS methods', fontsize=16)
ax[2].legend(bbox_to_anchor=[0.55,.6])
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52aec69350>
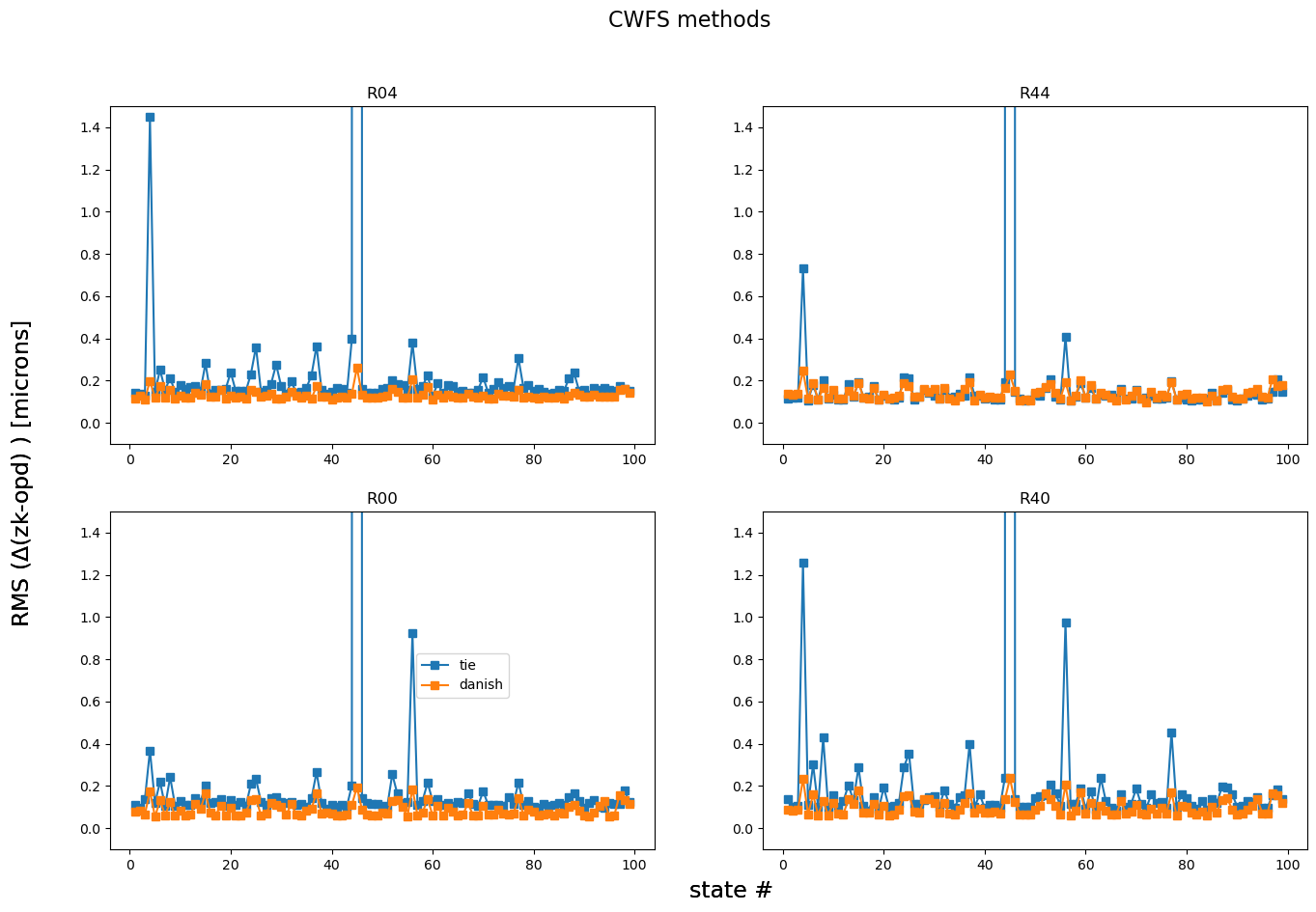
Also plot the AOS contribution to PSF degradation:
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(16,10))
ax = np.ravel(axs)
for method in rmss.keys():
i=0
for raft in rafts:
ax[i].plot(results[algo].keys(), psfDeg[method][raft], marker='s', label=f'{method}')
ax[i].set_title(raft)
ax[i].set_ylim(0.3,1.5)
i+=1
fig.text(0.5,0.06,'state #', fontsize=17)
fig.text(0.06,0.5, r'PSF FWHM AOS contribution ) [asec] ', rotation=90, fontsize=17, va='center')
fig.suptitle('CWFS methods', fontsize=16)
ax[2].legend(bbox_to_anchor=[0.55,.6])
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52aebfb010>
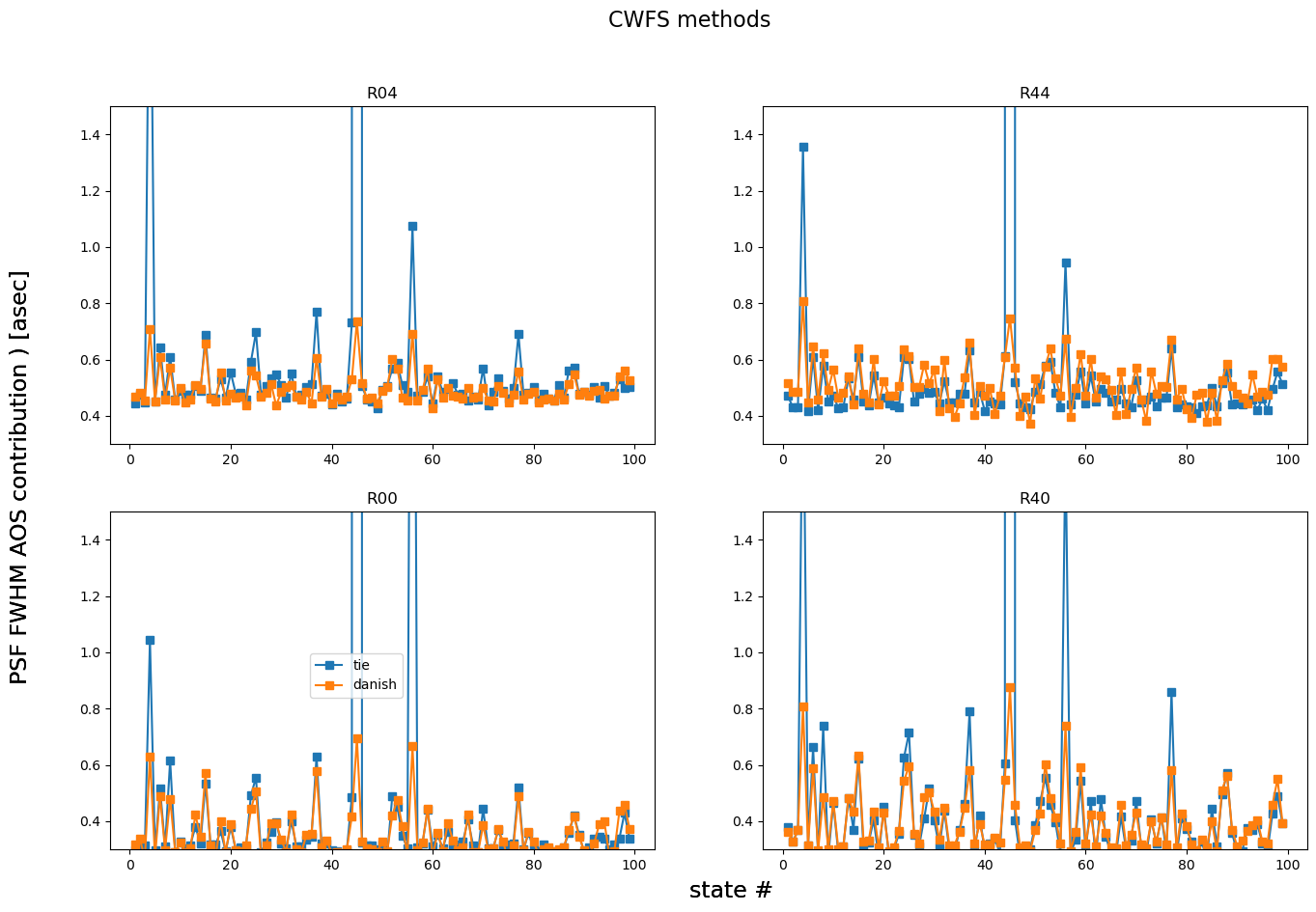
This shows that there is a state (possibly a few) that’s worse than others. Plot everything apart from that state:
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(16,10))
ax = np.ravel(axs)
for method in rmss.keys():
i=0
for raft in rafts:
mask = np.array(rmss[method][raft]) < 10
states_select = np.array(list(results[method].keys()))[mask]
rmss_select = np.array(rmss[method][raft])[mask]
ax[i].plot(states_select, rmss_select, marker='s', label=f'{method}')
ax[i].set_title(raft)
i+=1
fig.text(0.5,0.06,'state #', fontsize=17)
fig.text(0.06,0.5,r'RMS ($\Delta$(zk-opd) ) [microns] ', rotation=90, fontsize=17, va='center')
fig.suptitle('CWFS methods', fontsize=16)
ax[2].legend(bbox_to_anchor=[0.55,.6])
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52ae9ab010>
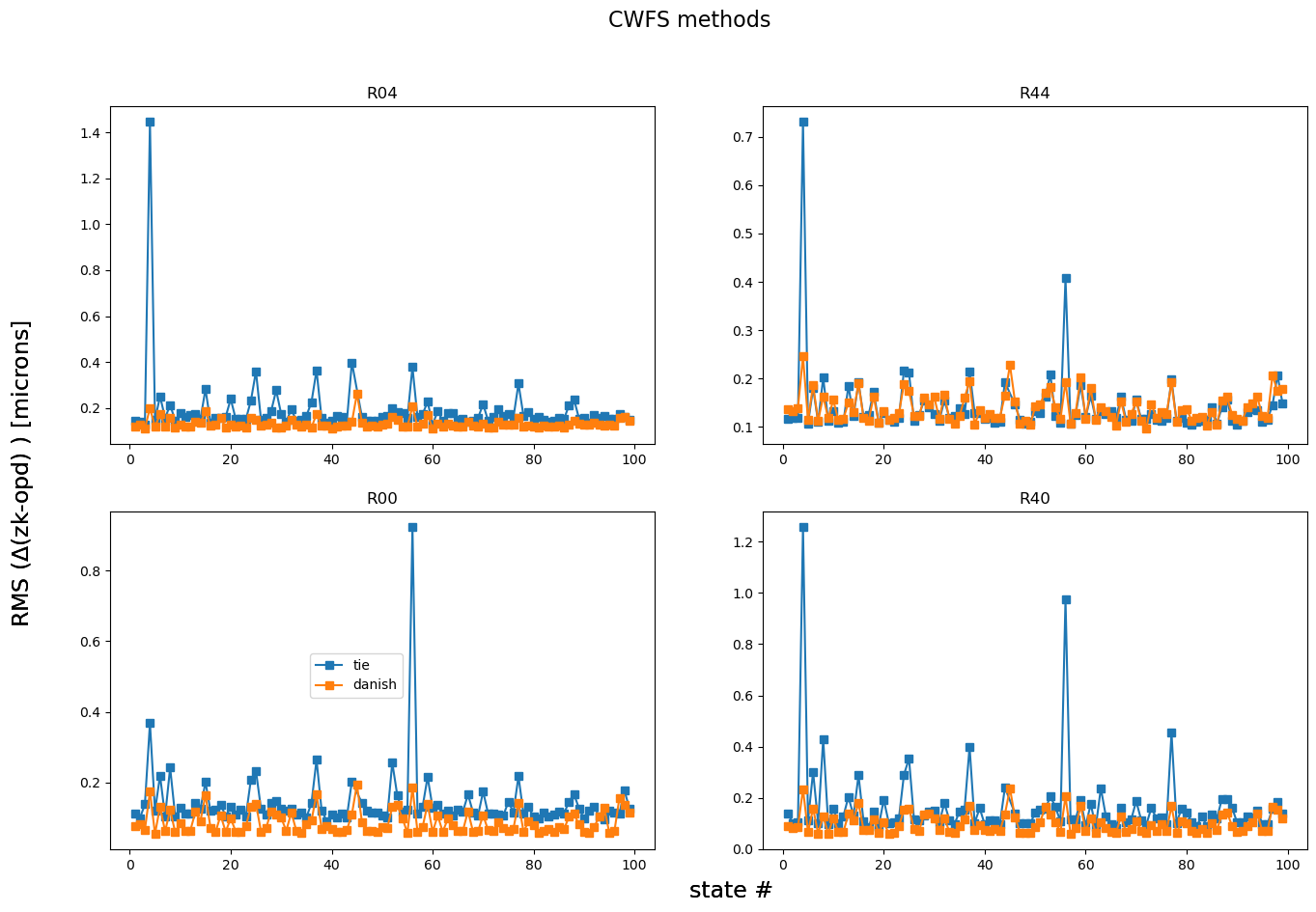
Focus on the errant state:
plot_lsstcam_fit_vs_opd(45, opd_raft_to_id, all_opd, results)
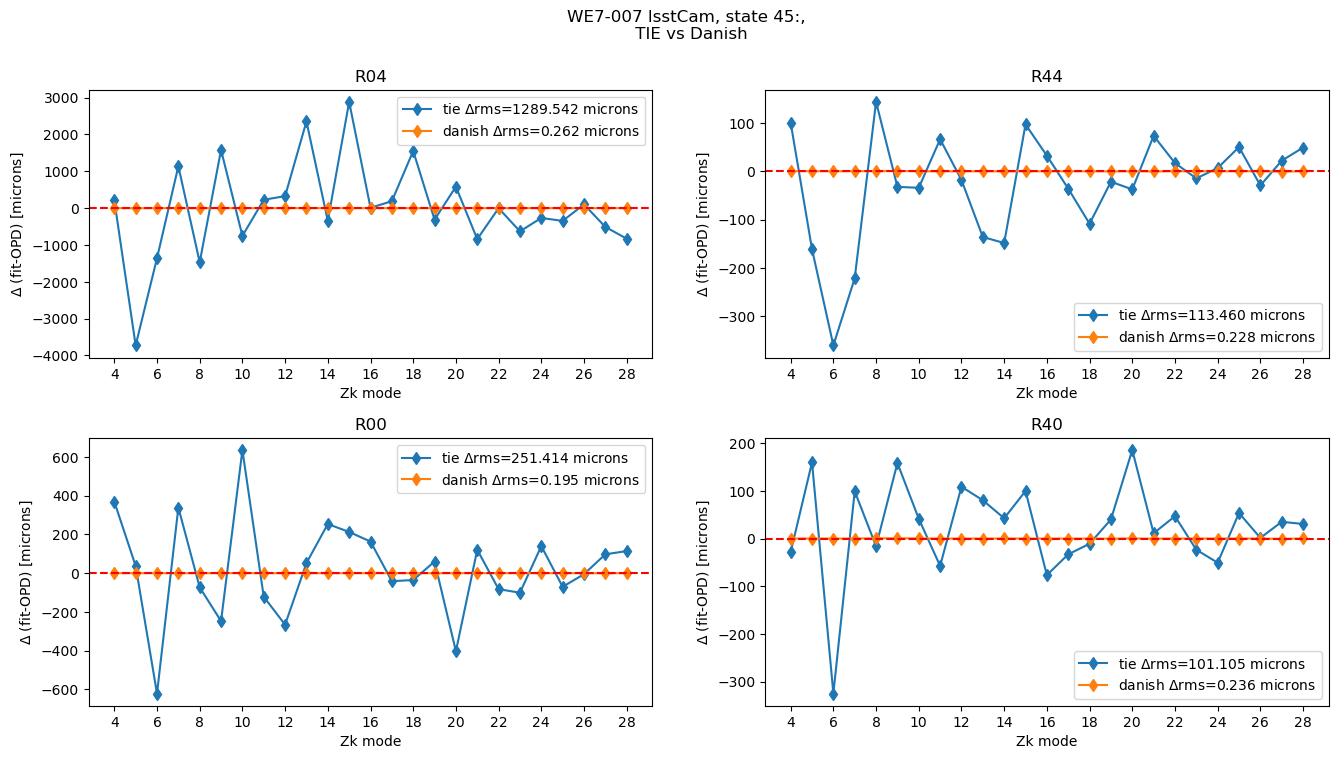
We see that while Danish has a result close to OPD, TIE is definitely suffering from a bad fit. Show the stamps used:
refs = list(registry.queryDatasets('donutStampsExtra', collections=[ 'WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' and detector.purpose='WAVEFRONT' and visit.seq_num = 2045").expanded())
zkRaw = butler.get('zernikeEstimateRaw', dataId= refs[0].dataId, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'])
zkRaw1 = butler.get('zernikeEstimateRaw', dataId= refs[0].dataId, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_Danish1'])
zkRaw[0]
array([-1.42689246e+01, -5.51136728e-01, 9.57510874e+01, 3.29284421e+00,
9.62738958e+00, 4.07373023e+00, -3.89940463e+01, 3.44553603e-01,
-1.48137946e+01, 1.52848648e+01, -1.34964708e+01, -1.59358651e+01,
4.72314172e-02, -7.45705165e+00, 9.54004421e-01, 1.35170286e+01,
1.51944589e+00, 1.87912801e+00, 3.71520720e+00, -3.81286751e+00,
5.28509294e+00, 6.23561188e+00, 2.34519833e+01, -5.02607643e+00,
-3.11757073e+01])
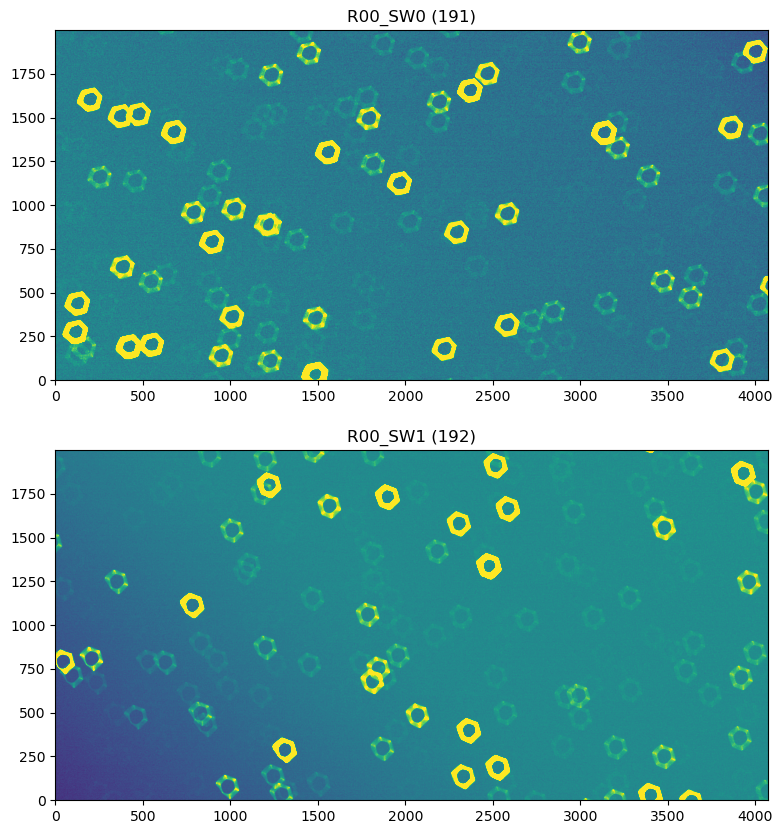
So these are gigantic values (in microns) ! Show the postISRCCD
dataIdExtra= {'instrument':'LSSTCam',
'detector':191,
'exposure':5024072302045,
'day_obs':20240723
}
dataIdIntra= {'instrument':'LSSTCam',
'detector':192,
'exposure':5024072302045,
'day_obs':20240723
}
exposureExtra = butler.get('postISRCCD', dataId = dataIdExtra, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_ISR'])
exposureIntra = butler.get('postISRCCD', dataId = dataIdIntra, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_ISR'])
fig,ax = plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(10,10))
k=0
for exposure in [exposureExtra,exposureIntra]:
zscale = ZScaleInterval()
d = exposure.image.array
vmin,vmax = zscale.get_limits(d)
ax[k].imshow(d, vmin=vmin,vmax=vmax, origin='lower')
ax[k].set_title(f'{exposure.getDetector().getName()} ({exposure.getDetector().getId()})')
k+=1
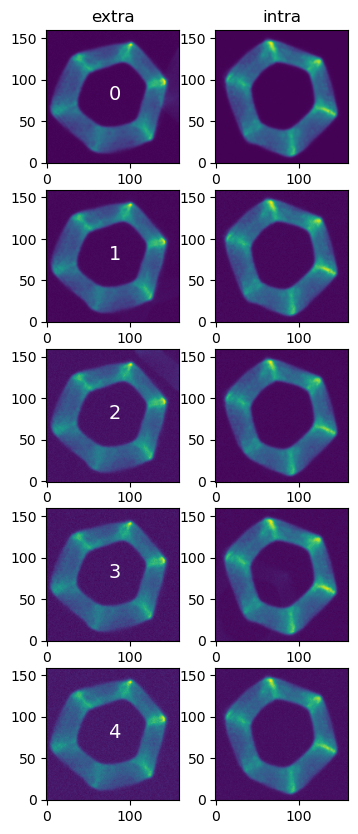
Compare the extra and intra-focal donuts
dataRefs = registry.queryDatasets('donutStampsExtra', collections=[ 'WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'],
where=f"instrument='LSSTCam' and detector.purpose='WAVEFRONT' and visit.seq_num = 2045").expanded()
refs = list(dataRefs)
donutStampsExtra = butler.get('donutStampsExtra', dataId=refs[0].dataId, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'])
donutStampsIntra = butler.get('donutStampsIntra', dataId=refs[0].dataId, collections=['WET-001_lsstCam_direct_TIE1'])
nrows=5; ncols=2
w=2
fig,ax = plt.subplots(nrows,ncols, figsize=(ncols*w, nrows*w))
for i in range(5):
de = donutStampsExtra[i]
di = donutStampsIntra[i]
ax[i,0].imshow(de.stamp_im.image.array, origin='lower')
ax[i,1].imshow(di.stamp_im.image.array, origin='lower')
ax[i,0].text(75,75,i, fontsize=14, color='white')
ax[0,0].set_title('extra')
ax[0,1].set_title('intra')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'intra')
Show OPD and Zernike fits for that exposure:
raft = refs[0].dataId.detector.raft
state = 45
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title(f'Optical state #{state}, raft {raft} , fit results' )
opdId = opd_raft_to_id[raft]
opd_zk = 0.001*np.array(all_opd[state][opdId][3:29])
ax.plot(np.arange(4,29), opd_zk, marker='d', label=f'OPD ')
# plot raw TIE
for i in range(len(zkRaw)):
ax.plot(np.arange(4,29),zkRaw[i], alpha=0.2, label=f'tie raw')
# plot raw Danish
for i in range(len(zkRaw1)):
ax.plot(np.arange(4,29),zkRaw1[i], alpha=0.4, ls='--', label=f'danish raw')
ax.set_ylim(-2,2)
ax.set_ylabel(r'Fit value [microns]')
ax.set_xlabel('Zk mode')
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(4,29,step=2))
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=[1.0,0.9], ncols=2)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52ae221650>
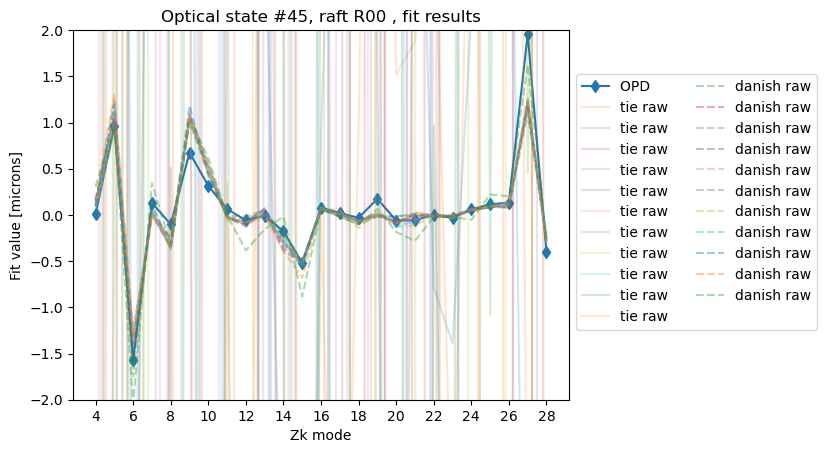
So for TIE all donut estimates for that state are exceptionally bad. Please see a parallel technote SITCOMTN-146 for the impact of the number of Zk modes fit on the fit result. Especially inclusion of Zk23-26 leads to a degradation of fit; hence the shift (around Nov 2024) towards fitting a sequence of Zk4:15, Zk18:22, Zk27:28 i.e. 4-28, excluding 16, 17, 23-26 (see estimateZernikes settings).
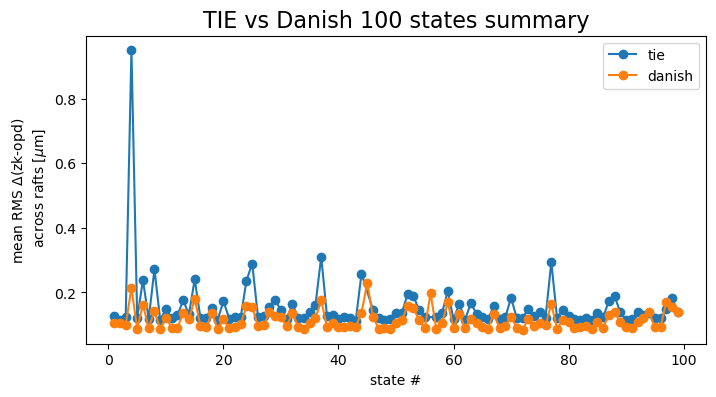
Marginalize across all detectors:
mean_per_state = {}
mean_per_state_psf = {}
for method in rmss.keys():
all_raft_data = []
all_raft_data_psf = []
for raft in rafts:
all_raft_data.append( rmss[method][raft])
all_raft_data_psf.append(psfDeg[method][raft])
mean_per_state[method] = np.mean(all_raft_data, axis=0)
mean_per_state_psf[method] = np.mean(all_raft_data_psf, axis=0)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(8,4))
j=0
cmap = cmaps['tab10']
for method in mean_per_state.keys():
mask = np.array(rmss[method][raft]) < 0.5
states_select = np.array(list(results[method].keys()))[mask]
mean_select = mean_per_state[method][mask]
ax.plot(states_select, mean_select, marker='o', label=f'{method}',
c=cmap(j))
j+=1
ax.set_xlabel('state #')
ax.set_ylabel(r'mean RMS $\Delta$'+'(zk-opd) \n across rafts '+r'[$\mu$m]',)
ax.set_title('TIE vs Danish 100 states summary', fontsize=16)
ax.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52ad1df050>
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(8,4))
j=0
cmap = cmaps['tab10']
for method in mean_per_state.keys():
mask = np.array(psfDeg[method][raft]) < 1
states_select = np.array(list(results[method].keys()))[mask]
mean_select = mean_per_state_psf[method][mask]
ax.plot(states_select, mean_select, marker='o', label=f'{method}',
c=cmap(j))
j+=1
ax.set_xlabel('state #')
ax.set_ylabel('mean PSF FWHM AOS contribution \n across rafts [asec] ')
ax.set_title('TIE vs Danish 100 states summary', fontsize=16)
ax.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f52ad35b010>
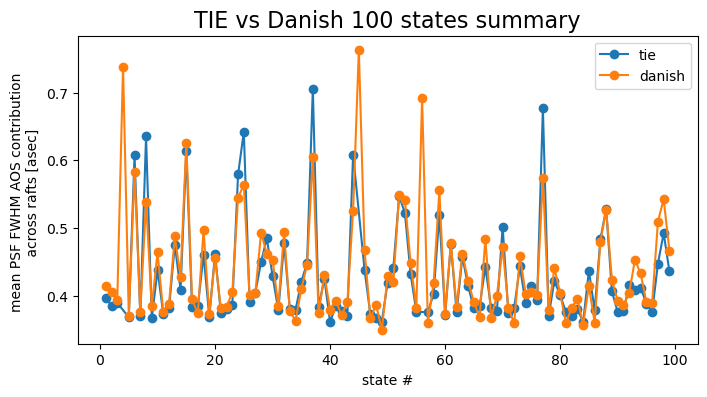
This shows that for majority of simulated states, Danish performs better than TIE in terms of an absolute fit value compared to the OPD in microns. However, when converted to PSF degradation, the difference is not as clear cut. Choice between Danish and TIE would need to consider the fit accuracy and robustness to outliers (eg. here for state 45 Danish was immune to being provided very distorted donuts).